Two-point function
Block name
B80_TWOPOINTFUNCTION
ST call
Version V1.0 PROGRAM TEST B80 VAR REAL1,REAL2: REAL; END_VAR REAL2 := LIB.CORE.V1_0.B80_TWOPOINTFUNCTION(IN:=REAL1, X1:=20,X2:=20,Y1:=0,Y2:=100); END_PROGRAM Version V1.1 PROGRAM TEST2_B80 VAR FB:LIB.CORE.V1_1.B80_TWOPOINTFUNCTION; IN_V:REAL; X1_V:REAL:=20; X2_V:REAL:=20; Y1_V:REAL:=0; Y2_V:REAL:=100; OUT_V:REAL; END_VAR FB(IN:=IN_V, X1:=X1_V, X2:=X2_V, Y1:=Y1_V, Y2:=Y2_V); OUT_V:=FB.OUT; END_PROGRAM
Library
LIB\CORE
Version
V1.1
Description
Linear function, recalculation of input value to output value defined by two points.
Inputs
| Input | Type | Description | Default value |
| IN | REAL | Input signal | 0 |
| X1 | REAL | 1.point, x coordinate | 20 |
| X2 | REAL | 2.point, x coordinate | 50 |
| Y1 | REAL | 1.point, y coordinate | 0 |
| Y2 | REAL | 2.point, y coordinate | 100 |
Outputs
| Output | Type | Description |
| OUT | REAL | Output signal |
| SIGN | BOOL | Sign of the output signal |
Function
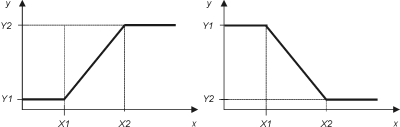
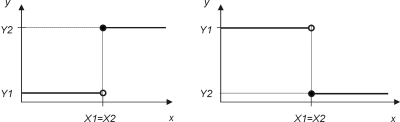
The block implements a transfer function given by two points, [X1,Y1] and [X2,Y2], see figure below. The points do not have fixed order, both X1<X2 and X1>X2 is possible. If X1=X2 then y=Y1 for x<X1, y=Y2 otherwise, see figure 2 below. The sign output is indicating the sign of the output signal y: When y>= 0 sign=true, otherwise sign=false.
Function may be rising or falling, [X1,Y1], [X2,Y2].
In case that X1=X2: value at x=X1=X2 is given by Y2.
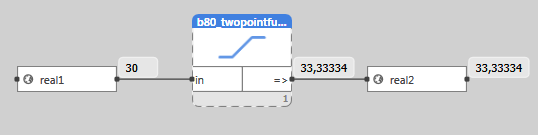
Application example
Older version
Version V1.0 was defined as a function. V1.1 is defined as a function block, therefore it can bes added to graphs and it can be set tu manual mode. Functionality remains without change.